STORAGE OF SOLIDS

Storage Solutions
Depending on the product´s density, requests and place of installation, we should apply one technology or another.
Specific solutions finished in stainless steel, aluminum, GRP, textile or carbon steel.
- Mobile or static devices
- Exterior or interior installation devices
- Silos up to three chambers
- Cleaning and drying designs for the interior of the silos
- Thermal insulation
- With sensors of maximum and minimum
- Load system for tanker trucks
Our Engineering team will contact you
In order to design an efficient storage system, we must take into account the different variables that can influence it:
- Density of the material(s) and its specific requirements.
- Place of installation and available space.
- Applicable regulations.
The design will not be the same for a granular material as for a powdery material, and the system we design will be different if it is located outdoors or inside a building. Likewise, the height of the equipment may be limited both by the climatic conditions of the area and by the town planning regulations of the locality in question, and we will not treat PVC in the same way as flour…
In storage systems, in general, three different phases must be distinguished:
- Procurement (collection and reception of raw materials).
- Intermediate products (processing).
- Finished product.
The system will be designed specifically for each of the phases and special care will be taken in the transport system used between them. And depending on the need, we can decide between mobile or static equipment:
- Mobile silos with capacities up to 360 litres.
- Static silos with capacities up to 500 m3.
- Static silos with agitator and capacities up to 40 m3.
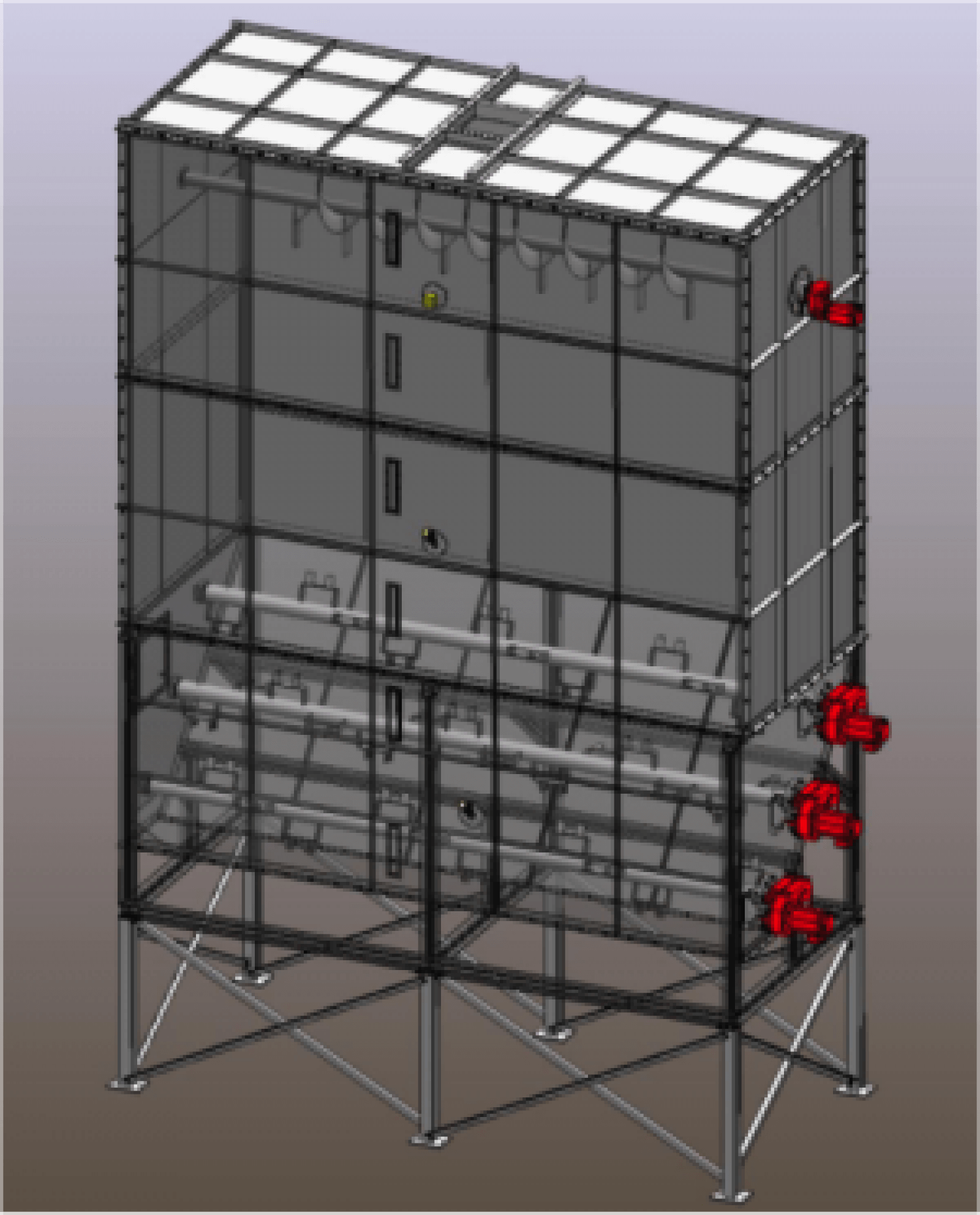
- Modular static silos with square section and agitator up to 60 m3.
We adapt the shape of the silos to the requirements of the product:
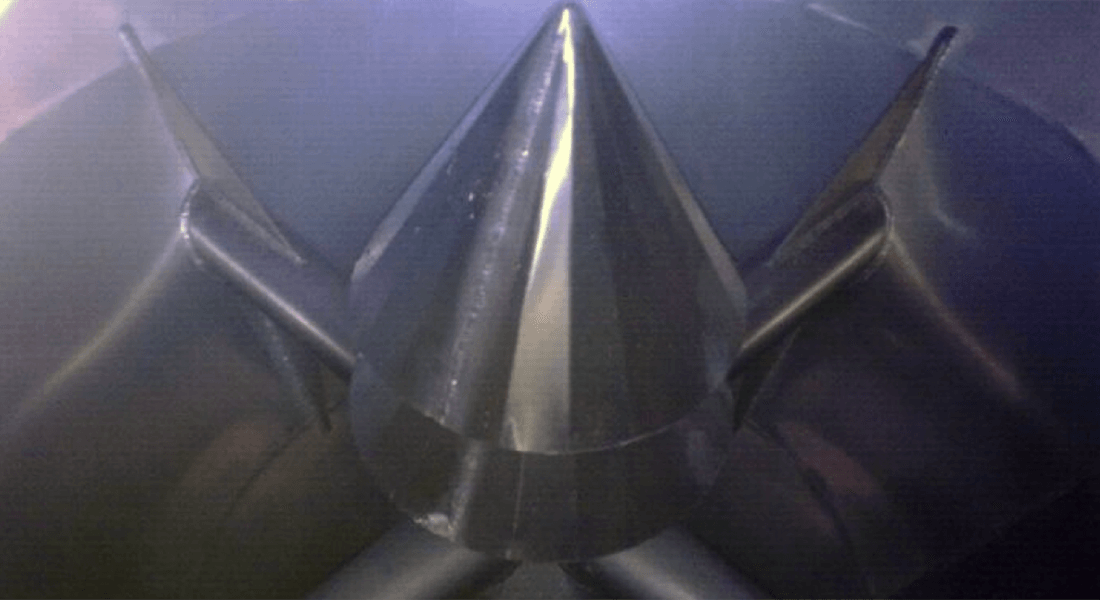
- Granular product, with apparent density between 0.6 and 0.9 Kg/dm3, in general we will use circular section silos with tubular or funnel flow, with discharge cone at 90º. Tubular flow consists of the formation of a flow channel aligned with the silo outlet, which is surrounded by a zone of material that initially remains static. In the discharge of a silo with tubular flow, the material does not move all at once.
“The advantages of this type of flow are less wear, since the friction due to the discharge is negligible, the pressure on the walls is low (which saves material in the construction of the silo), and the abrasion on the walls is lower than in other cases. In addition, and due to the degree of the discharge cone, we have greater storage capacity with the same height. In general, it is a more economical silo”. - Pulverulent product, with apparent density over 1-3 Kg/dm3, we can use circular or rectangular section silos with mass or mass flow, with a discharge cone of up to 20º. Mass flow means that at the moment of discharge all the stored product is in movement and respects the ‘first in-first out’ principle, and for this it is very important to design the shape and angle of the outlet as well as a suitable outlet diameter.
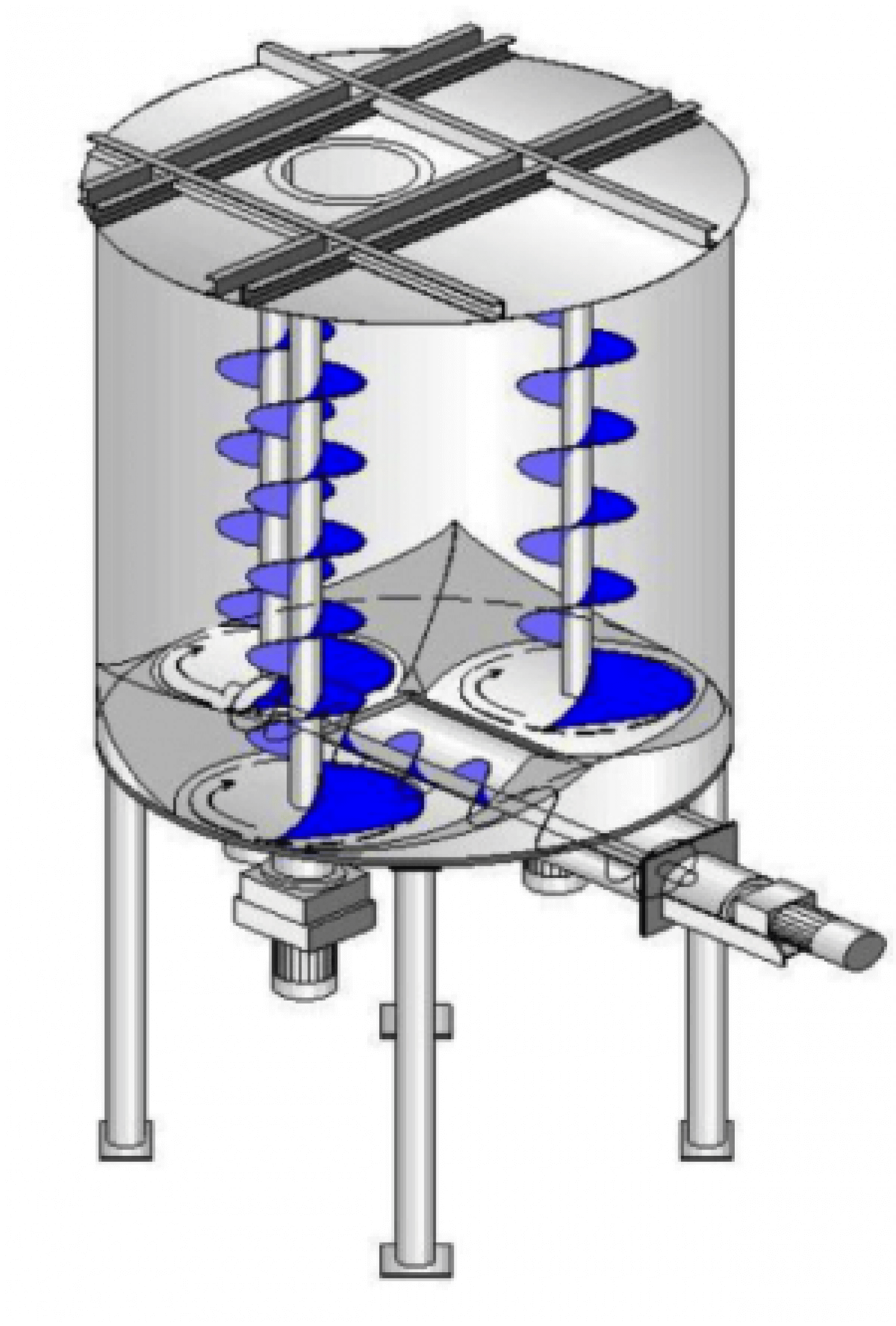
“It is also very important to have the right surface finish on the inside walls of the silo, because the more friction, the greater the adherence and therefore the larger the outlet diameter, and with less cone degrees, vaults, chimneys and dead zones will be avoided. This is a silo with a higher economic cost”. - Product in flakes or flakes, with apparent density between 0.02 and 0.3 Kg/dm3, and lengths of up to 30 mm, we will use a cylindrical section, flat-bottomed silo with three internal motorised agitators and a mechanical extraction system by means of a screw conveyor.
“The agitators ensure that the product is in continuous movement and does not clump, making it easier to extract the product”.
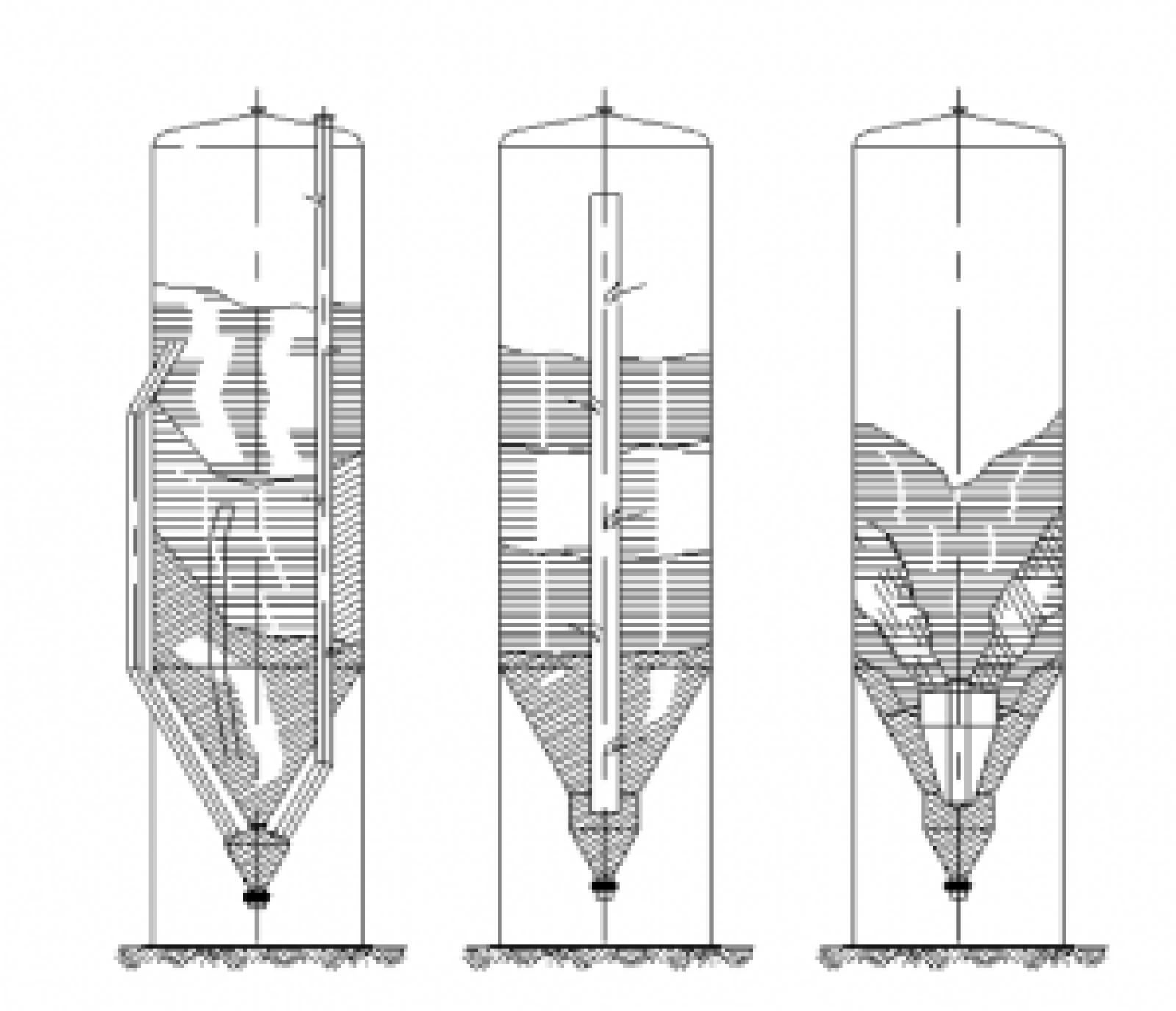
Types of storage silos and materials
- Carbon steel
- Stainless steel AISI 304 for standard solutions and AISI 316L for food, pharmaceutical or fine chemical applications
Aluminium - GRP (glass fibre reinforced plastic) for volumes up to 1500 m3
- Trevira type textiles, up to 100 m3
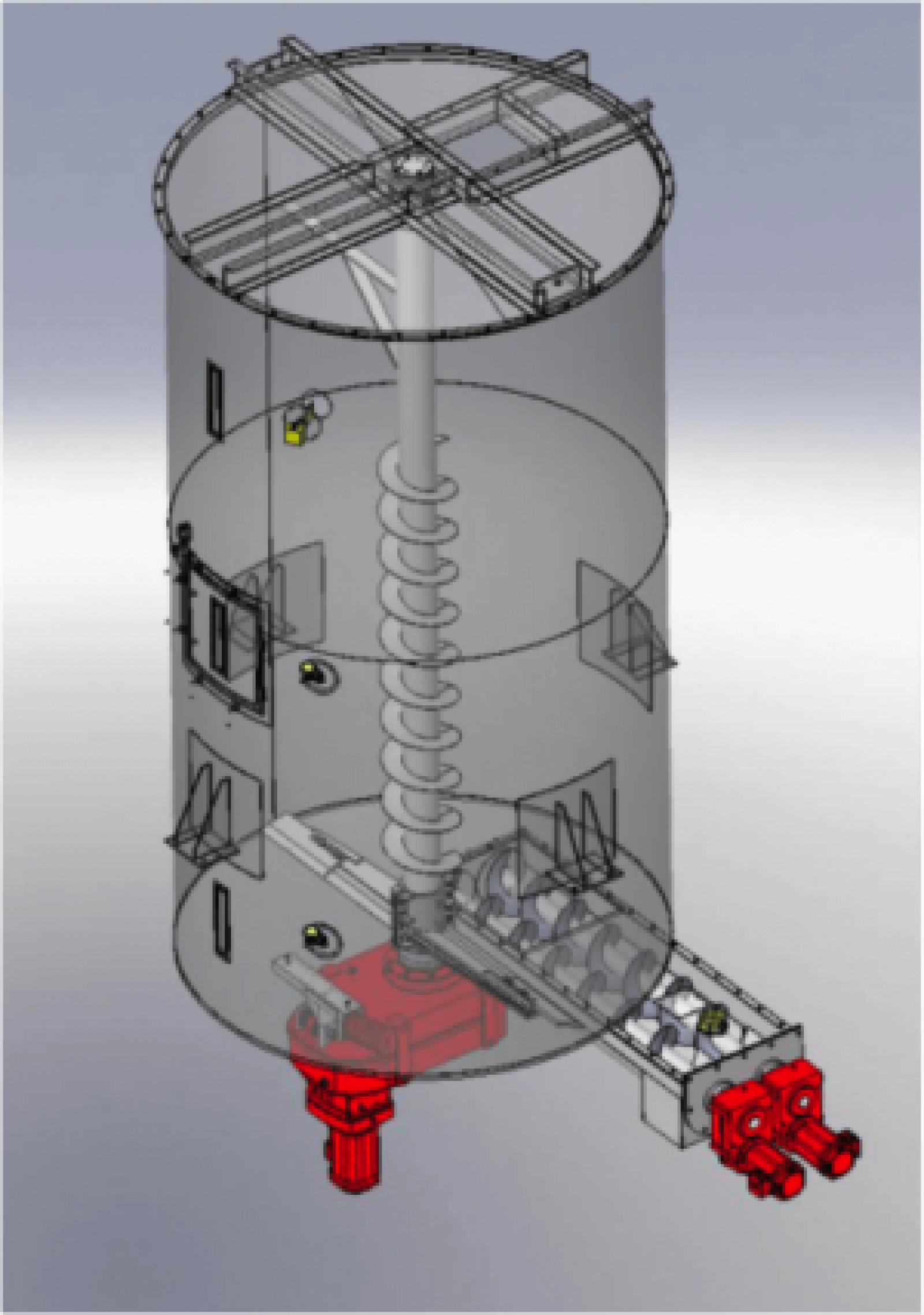
1. Special silo for fibres, with apparent density between 50 and 100 g/dm3 and fibre lengths between 10-30 mm, we will use a cylindrical section silo with a flat bottom, with a central agitator and a scraper whose mission is to dose the material to the screw conveyor for its extraction. We can equip this silo with up to three screw conveyors, each with its own discharge mouth. This type of silo can also be used for some types of powders and flakes.
2. Mixing silos, also called homogenisers. We can use them with a cylindrical or rectangular section and they are generally used in the supply phase and in the finished product phase. In the supply phase, they are used to homogenise the product before consumption or transformation, and finally, in the finished product phase, they are used to homogenise the product before delivery to the customer or bagging.
“Depending on the size, this type of silos has the advantage of covering two tasks, storage and homogenisation.”
“We offer modular silos with the electric motors integrated in the silo itself, and also cylindrical silos with different internal geometries that allow us, by means of an external drive, to re-circulate the product as many times as necessary to achieve the optimum level of homogenisation.”
“Our offer includes silos with up to three chambers, silos with reinforced or non-reinforced skirt for the placement of load cells and silos with a self-supporting structure. Any of our silos can be equipped with symmetrical or asymmetrical cones, conical trunk, pyramidal trunk, or square base.”

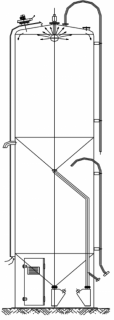

Silo accessories
We include the complete installation with instrumentation, control and wiring:
- Lightning arrester and anemometer.
- Accesses for cleaning and inspection, ladders, peepholes and lighting.
- Level control: visual, vane, plumb line, guided radar, etc.
- Bag filter.
- Direct weighing systems by means of load cells.
- ATEX solutions.
- Safety valves for overfilling.
- Depression valves to prevent implosions due to vault collapse.
- Metallic and non-metallic particle detectors.
- Dust collection systems.
- Extraction systems and elements.
- Filling systems.
- Fluidisation elements.
- Heating and insulation.
- Automatic internal cleaning and drying.
- Dehumidification and tropicalisation according to the requirements of the material or the environment.

European regional development fund
A way to make europe
Coscollola Engineering SL, within the framework of the ICEX Next Program, has received support from ICEX and co-financing from the European FEDER fund. The purpose of this support is to contribute to the international development of the company and its environment.